Hair loss is a common condition affecting many people worldwide. It is aesthetically distressing and linked to a variety of physiological and psychological factors. This comprehensive guide covers everything you need to know about hair loss, from understanding the nature of hair growth to common causes, symptoms and treatment options.
Understanding Hair Loss
Hair loss, medically known as alopecia, refers to the loss or thinning of hair on the scalp or body. It is a condition that affects both men and women and can occur at any age. Hair loss can range from mild, manifested as patches of baldness, to severe, leading to complete baldness.
It is important to remember that daily hair loss or shedding is part of the normal hair growth cycle. Each hair follicle goes through a growth phase (anagen), a resting phase (telogen) and a shedding phase (exogen). During the shedding phase, old hair is shed to make room for new hair. However, hair loss occurs when the rate of shedding exceeds the rate of regrowth or when the new hair becomes noticeably thinner.
There are various types of hair loss, each with its own causes and characteristics. Androgenetic alopecia, or male or female pattern baldness, is the most common form of hair loss. It is typically characterized by a receding hairline in men and thinning hair in women. Other types of hair loss include alopecia areata, which presents as patchy hair loss, and telogen effluvium, which is often triggered by stress, illness or hormonal changes.
Many factors can contribute to hair loss. Genetics plays an important role, as certain genes can make individuals more susceptible to hair loss. Hormonal imbalances, such as those experienced during pregnancy or menopause, can also lead to hair loss. Medical conditions such as thyroid disorders and autoimmune diseases can also affect hair growth. External factors such as excessive hair styling, harsh chemicals and tight hairstyles can damage hair follicles and contribute to hair loss.
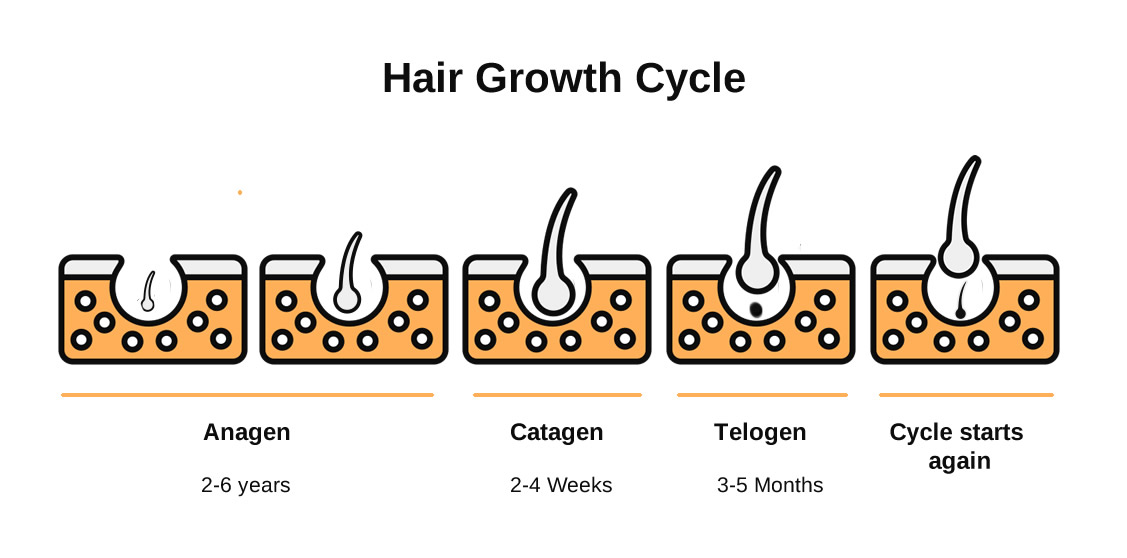
Hair Growth Stages
Usually most of our hair is in the growth phase and only a small percentage is in transition or resting phases.
Growth Phase: During the growth phase, hair follicles actively produce new cells, pushing existing hair strands upwards and outwards. This is the phase when our hair grows the longest and thickest. The duration of the growth phase varies from person to person, but typically lasts between two and seven years.
Transition Phase: After the growth phase, hair follicles enter the transition phase. This short period lasts only a few weeks, during which the hair follicles shrink and separate from the blood supply. The hair strands stop growing at this stage and prepare for the resting phase.
Resting Phase: The resting phase, also known as the telogen phase, is a very important part of the hair growth cycle. During this phase, hair follicles are dormant and no new hair growth occurs. Instead, the existing hair strands remain in place until they are pushed out by new hair growth in the next growth phase. The resting phase typically lasts about three to four months.
However, various factors can disrupt this normal hair cycle, causing more hair to enter the resting phase earlier than usual. These factors include hormonal changes, medications, stress, nutritional deficiencies and underlying health problems. When more hair follicles enter the resting phase early, it leads to increased hair loss and hair loss.
Hormonal changes, such as those that occur during pregnancy or menopause, can affect the hair growth cycle. Fluctuations in hormone levels can cause more hair follicles to enter the resting phase, leading to temporary hair loss. Similarly, certain medications, such as chemotherapy drugs, can disrupt the hair growth cycle and lead to hair loss.
Stress is another important factor that can affect hair growth. High levels of stress can trigger telogen effluvium, where many hair follicles enter a resting phase at the same time. This can cause noticeable thinning and hair loss.
Nutritional deficiencies, especially iron, zinc and biotin, can also affect the hair growth cycle. These nutrients play an important role in hair health and growth. When deficient, hair follicles may enter the resting phase prematurely, leading to increased hair loss.
In addition, certain underlying health conditions such as thyroid disorders and autoimmune diseases can disrupt the hair growth cycle. These conditions can cause imbalances in the body, affecting the normal functioning of hair follicles and leading to hair loss.
Causes of Hair Loss
Understanding the causes of hair loss is crucial to finding practical solutions and treatments. Let’s take a deeper dive into the common causes:
- Genetic predisposition: This is the most common cause of male and female pattern baldness, where hair loss is inherited from one’s parents. Suppose your parents or close relatives have experienced hair loss. In this case, you are more likely to be genetically predisposed to it. This hair loss typically occurs gradually over time, with the hairline receding or thinning at the crown. A combination of genes from both parents usually influences the genetic predisposition to hair loss. While genetics plays an important role, it is important to remember that other factors can also contribute to the severity and progression of hair loss.
- Hormonal changes: Pregnancy, childbirth, menopause and thyroid problems can cause significant hormonal changes, leading to temporary or permanent hair loss. During pregnancy, hormonal fluctuations can cause an increase in hair thickness and growth. However, after giving birth, many women experience postpartum hair loss, which is a normal part of the growth cycle. Menopause causes a drop in estrogen levels, which can contribute to hair thinning and loss. Thyroid imbalances such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism can also disrupt the normal hair growth cycle and cause hair loss.
- Nutritional deficiencies: Lack of essential nutrients such as iron, protein and vitamins can cause hair loss. Our hair follicles need a steady supply of nutrients to maintain healthy growth. Inadequate intake or absorption of critical nutrients can weaken hair follicles, leading to hair thinning and hair loss. A balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-rich foods is essential to support healthy hair growth. Iron-rich foods such as green leafy vegetables, lean meats and protein sources such as eggs and legumes can help nourish hair follicles and support optimal hair health.
- Stress: High levels of stress can lead to certain types of hair loss. Stress-induced hair loss, also known as telogen effluvium, occurs when a significant amount of hair enters the resting phase of the hair growth cycle prematurely. This can lead to excessive shedding and noticeable thinning of the hair. In addition, chronic stress can further contribute to hair loss by disrupting the body’s hormonal balance. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, exercise and support from loved ones can help reduce its impact on hair health.
- Medical conditions: Some diseases, such as diabetes and lupus, can cause hair loss. These medical conditions can disrupt the normal functioning of the body, affecting various systems, including hair growth. Hair loss associated with underlying medical conditions may require specialized treatment and management. If you suspect that an underlying medical condition is causing your hair loss, it is very important to consult a healthcare professional. They can provide a comprehensive assessment and recommend appropriate interventions.
- Lifestyle Factors: Unhealthy lifestyle habits such as poor diet, insufficient sleep, excessive alcohol consumption and smoking can also contribute to hair loss. A diet lacking in essential nutrients can affect the health and vitality of your hair. Similarly, chronic stress and unhealthy coping mechanisms such as smoking can create hormonal imbalances, leading to hair loss.
- Medical Conditions and Hair Loss: Various skin conditions such as alopecia areata, psoriasis and seborrheic dermatitis can cause hair loss. Systemic diseases such as diabetes and lupus can also cause hair loss. Treatment of these conditions usually focuses on managing symptoms and controlling the disease process to help reduce hair loss.
- Hair Care Practices: Improper hair care practices can also lead to hair loss. This includes excessive heat styling tools, hair dye, and harsh hair products that can damage hair follicles and lead to temporary or permanent hair loss. Therefore, it is very important to treat your hair with care to prevent hair loss.

What is Good for Hair Loss?
- Healthy Diet: A balanced and nutrient-rich diet can improve hair health. Focus on foods rich in vitamins, minerals, proteins and healthy fats. Omega-3 fatty acids, biotin, zinc, iron and vitamin D are especially important for hair growth.
- Gentle Hair Care: Avoid aggressive styling, excessive heat and harsh chemicals that can damage hair and weakening follicles.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can contribute to hair loss. Engage in relaxation techniques such as meditation, yoga, deep breathing or mindfulness to reduce stress levels.
- Medications: Over-the-counter topical treatments such as minoxidil (Rogaine) and prescription medications such as finasteride (Propecia) can help slow hair loss and promote regrowth in some people.
- Laser Treatment: Low-level laser therapy (LLLT) devices emit red light to stimulate hair follicles and improve blood circulation, potentially leading to hair growth.
- Essential Oils: Some essential oils such as rosemary, peppermint and lavender are believed to promote hair growth when applied topically. However, scientific evidence is limited and it is important to use them safely.
- Nutritional Supplements: Supplements containing biotin, vitamins and minerals can complement a healthy diet. Consult a health care professional before starting any supplements.
- Acupuncture: Acupuncture can improve blood circulation for some people.
- and is an alternative therapy believed to be able to stimulate hair growth. Limited scientific evidence supports this claim.
What are the Oils Good for Hair Loss?
Which oils can we use for hair loss?
- Rosemary Oil: Rosemary oil is believed to increase blood circulation to the scalp, which can stimulate hair growth. It also has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that can help improve scalp health.
- Lavender Oil: Lavender oil has been studied for its potential to promote hair growth and reduce hair loss. Its calming scent may also help reduce stress, a potential contributor to hair loss.
- Peppermint Oil: Peppermint oil contains menthol, which can stimulate blood flow to the scalp and promote hair growth. It is also known for its cooling sensation.
- Cedarwood Oil: Cedarwood oil shows promise in promoting hair growth by improving circulation to the scalp and promoting hair follicle health.
- Thyme Oil: Thyme oil is believed to have properties that can promote hair growth by improving blood circulation and helping to prevent hair loss.
- Tea Tree Oil: Tea tree oil has anti-fungal and antibacterial properties that can help maintain a healthy scalp. It can be useful if hair loss is caused by scalp conditions such as dandruff or fungal infections.
- Sage Oil: Sage oil can help balance hormones and reduce stress, which may indirectly affect hair loss.
- Jojoba Oil: Although not technically an essential oil, jojoba oil is often used as a carrier oil for essential oils. It is very similar to natural sebum and can help moisturize the scalp.
What are the Vitamins Good for Hair Loss?
Which vitamins can we use for hair loss?
- Vitamin A: Vitamin A promotes the production of sebum, an oily substance that helps keep the scalp moisturized. It also helps the growth of healthy cells, including hair cells. However, excessive vitamin A intake can have negative effects, so it is important to maintain a balanced level.
- Vitamin D: Vitamin D is essential for the hair follicle cycle and plays a role in hair follicle health. Spending time in the sun and consuming vitamin D-rich foods can help maintain adequate levels.
- Vitamin E: Vitamin E is an antioxidant that helps protect the scalp from oxidative stress. It can also support hair growth by promoting blood circulation to the scalp.
- Vitamin B Complex: B vitamins, including biotin (B7), niacin (B3), pantothenic acid (B5) and others, are essential for healthy hair growth. Biotin, in particular, is often associated with hair health and deficiencies can lead to hair thinning.
- Vitamin C: Vitamin C is an antioxidant that helps protect hair follicles from damage caused by oxidative stress. It also helps in the production of collagen, which is important for hair structure.
- Vitamin K: Vitamin K contributes to healthy blood circulation, which supports the delivery of nutrients to the hair follicles.
- Folic Acid (Vitamin B9): Folic acid is involved in cell division and tissue growth, which are critical processes for hair growth.
- Iron: Iron is essential for carrying oxygen to cells, including hair follicles. Iron deficiency (anemia) can lead to hair loss and hair thinning.
- Zinc: Zinc is involved in the production of DNA and RNA, which are important for the division and function of hair follicle cells. Zinc deficiency can lead to hair loss.
- Selenium: Selenium is an antioxidant that helps protect hair follicles from damage and supports a healthy immune system.
Treatment Options for Hair Loss
Treatment options are generally as follows:
- Medication: Some medications, such as minoxidil and finasteride, can slow hair loss and even help regrow lost hair to some extent.
- Laser treatment: This treatment option uses low-level lasers to boost hair growth.
- Hair transplantation: Hair transplantation is often the last resort to treat hair loss. It involves transferring hair from an area where it is abundant to a bald or thinning area.
- Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: PRP therapy involves using the patient’s own platelet-rich plasma to stimulate hair follicles and promote regrowth.

Which Doctor Should I Go to for Hair Loss?
If you are experiencing hair loss and are looking for professional help, there are various departments you may consider consulting, depending on the possible causes and treatments for your hair loss. Skin and Venereal Diseases (Dermatology) is one of them.
- Dermatologist: Dermatologists are medical doctors who specialize in diseases of the skin, hair and nails. They are often the first choice to address hair loss. Dermatologists can diagnose the cause of your hair loss and recommend appropriate treatments, both medical and surgical.
- Trichologist: Trichologists are specialists who focus specifically on hair and scalp problems. They can provide in-depth assessments of hair and scalp health and recommend treatments and regimens to improve hair health.
- Endocrinologist: If your hair loss is related to hormonal imbalances or conditions such as thyroid disorders, an endocrinologist may be a good choice. They specialize in health issues related to hormones.
- Rheumatologist: If you suspect that an autoimmune condition such as alopecia areata may be causing your hair loss, a rheumatologist can diagnose and manage autoimmune disorders.
- Nutritionist or Dietitian: Nutritional deficiencies can contribute to hair loss. Consulting a nutritionist or dietitian can help you address dietary factors that may be affecting your hair health.
What tests are done for hair loss?
When you experience hair loss, a variety of tests may be performed to determine the underlying cause and help guide appropriate treatment. The specific tests recommended will depend on your symptoms, medical history and potential contributing factors.
Here are some common tests that can be done for hair loss:
- Physical Examination: A doctor will visually examine your scalp and hair to assess the pattern and extent of hair loss. They may also look for signs of inflammation, scaling or other scalp conditions.
- Medical History: Your doctor will ask about your family history of hair loss, recent illnesses or surgeries, medications you are taking, and your general health.
- Blood test: A blood test can help identify possible causes of hair loss, for example:
- Complete Blood Count (CBC): A test to check for anemia and other blood disorders.
- Thyroid Function Tests: A test to assess thyroid hormone levels.
- Hormone Levels: Hormonal imbalances can contribute to hair loss. Tests may include measurements of testosterone, estrogen and other related hormones.
- Iron and Ferritin Levels: Low iron levels can lead to hair loss.
- Vitamin and Mineral Levels: Deficiencies in vitamins such as vitamin D, vitamin B12 and minerals such as zinc can affect hair health.
- Antinuclear Antibody (ANA) Test: To check for autoimmune conditions that can cause hair loss.
- Scalp Biopsy: A small skin sample is taken from the scalp for analysis. This can help diagnose conditions that affect the hair follicles.
- Microscopic Examination: Hair and scalp samples can be examined under a microscope to identify any abnormalities.
- Hormone Tests: If hormonal imbalances are suspected, specific hormone tests can be performed to determine the levels of various hormones.
- Trichoscopy: This is a non-invasive method that uses a special magnifying device to examine the scalp and hair follicles.
- Phototrichogram: This test involves taking close-up photographs of the scalp and counting the hair to determine density and growth rate.
- Fungal Culture: If a fungal infection is suspected, a culture can be taken from the scalp to determine the presence of fungus.
- Genetic Testing: In some cases, genetic testing can help determine your predisposition to certain types of hair loss, such as male or female pattern baldness.